MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS - online book
The History And Development Of Musical Instruments From The Earliest Times.
| Share page | Visit Us On FB |
|
CHAPTER VIII. |
||
|
The construction of the organistrum requires but little explanation. A glance at the finger-board reveals at once that the different tones were obtained by raising the keys placed on the neck under the strings, and that the keys were raised by means of the handles at the side of the neck. Of the two bridges shown on the body, the one situated nearest the middle was formed by a wheel in the inside, which projected through the sound-board. The wheel which slightly touched the strings vibrated them by friction when turned by the handle at the end. The order of intervals was c, d, e,f,g, a, b-flat, b-natura/, c, and were obtainable on the highest string. There is reason to suppose that the other two strings were generally tuned a fifth and an octave below the highest. The organistrum may be regarded as the predecessor of the hurdy-gurdy, and was a rather cumbrous contrivance. Two persons seem to have been required to sound it, one to turn the handle and the other to manage the keys. Thus it is generally represented in mediaeval concerts.
The monoclwrd (p. 100) was mounted with a single string stretched over two bridges which were fixed on an oblong box. The string could be tightened or slackened by means of a turning screw inserted into one end of the box. The intervals of the scale were marked on the side, and were regulated by a sort of movable bridge placed beneath the string when required. As might be expected, the |
||
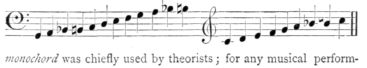 |
||